Navigating the world of infections is like exploring a jungle full of surprises. You’ve probably encountered thrush, a common fungal infection, but are you aware if it’s contagious?
In this article, you’ll unearth the facts about thrush. We’ll delve into its symptoms, causes, and ways it can be transmitted, as well as how to prevent it.
So, strap on your explorer’s hat, it’s time to demystify the candida jungle!
What Is Thrush?
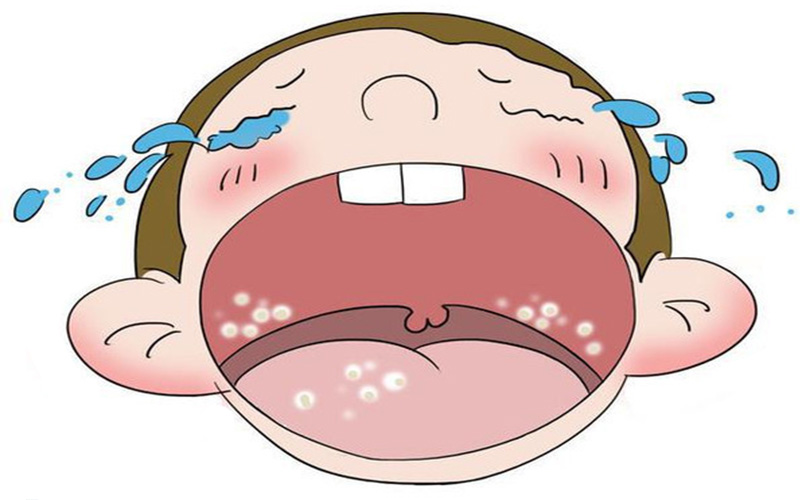
Thrush is an infection caused by the candida fungus, also known as yeast, that can occur in the mouth and other body parts. White bumps inside the mouth characterize it and is more common in those with weakened immune systems.
Now, let’s discuss the symptoms of thrush to understand it better.
What are the symptoms of thrush?
You might notice symptoms of thrush, such as white raised lesions on your tongue and cheeks, a cottony feeling in your mouth, or even a loss of taste. These signs can sometimes be mistaken for other conditions, so it’s essential to be aware of other symptoms.
You may also experience:
- Redness or soreness in your mouth can lead to difficulty swallowing or a feeling of food getting stuck in your throat.
- Cracks at the corners of your mouth, which can be particularly painful.
- A change in your sense of taste or a loss of taste altogether.
- In severe cases, you may develop a fever if the infection has spread beyond your mouth.
How do you get thrush?
Despite taking precautions, you might still end up with thrush if you come into close contact with someone who has it or if factors such as stress, certain medications, or health conditions disrupt the natural balance of bacteria and yeasts in your body.
Some medications, like antibiotics or corticosteroids, can kill off the helpful bacteria that keep Candida from proliferating. Illnesses such as diabetes or HIV can also make you more susceptible to thrush by weakening your immune system.
Poor oral hygiene, wearing dentures, and smoking can all create an environment where thrush thrives. Lastly, hormonal changes during pregnancy can upset the balance of microorganisms in your body, making you more prone to this condition.
Is thrush contagious?
In considering whether thrush is contagious, it’s important to understand that while it’s not typically seen as a highly infectious condition, it can be spread through close contact. Particularly, if you share utensils or cups or kiss someone whose oral thrush, you’re at risk of getting the infection.
Let’s clarify a few points:
- Direct contact with the infection, such as during breastfeeding, can transmit thrush.
- It’s not a condition that’s easily passed on, like the common cold or flu.
- People with weakened immune systems are more susceptible.
- Good oral hygiene can help prevent its spread.
How is thrush tested and treated?
While good hygiene and avoiding close contact can help prevent the spread of thrush, if you suspect you’ve contracted it, prompt testing and treatment are essential. Your doctor can diagnose thrush by examining your mouth and taking a small sample to confirm the presence of the candida fungus. If the infection has spread beyond your mouth, additional tests like throat cultures or endoscopy might be necessary.
Once diagnosed, treatment usually involves antifungal medications such as clotrimazole, miconazole, or nystatin, which you’ll use in your mouth for 7-14 days. If your immune system is weakened, fluconazole might be prescribed. Generally, thrush responds well to treatment, but recovery may take longer if your immune system is compromised.
How to prevent thrush?
So, how can you effectively prevent thrush?
- Maintain good oral hygiene: Brush regularly, floss daily, and use mouthwash. Replace your toothbrush frequently, and don’t share it with others.
- Eat a balanced diet: Limit sugar intake as yeast thrives on sugar. Include yogurt or other probiotic foods in your diet to maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in your body.
- Be cautious with antibiotics: While these medications are sometimes necessary, use them sparingly as they can disrupt your normal body flora, leading to thrush.
- Manage your health conditions: If you have a condition like diabetes or HIV that weakens your immune system, keep it under control to prevent infections like thrush.
Incorporating these steps into your daily routine can help keep thrush at bay.
Conclusion
In summary, thrush isn’t your average infection. It’s a sneaky, contagious culprit that loves damp, warm places.
You can contract it through close contact, but don’t fret! Armed with the right knowledge, you can become a fortress against this fungal foe.
Keep your hygiene top-notch and your immune system fighting fit to keep thrush at bay.
Remember, knowledge is power, and you’ve got what it takes to outsmart this sly invader.
Reference: